# 一、Vuex
# 1.1vuex是什么?什么作用?
vuex是状态管理工具,用于多个组件之间进行状态共享。vuex可以看成一个大管家,管理着一些全局使用的数据(头像,昵称等)。还是响应式的
简单原理:
- 不能进行响应式
const shareObj = {
name: 'qmj'
}
Vue.prototype.shareObj = shareObj
# 1.2状态管理什么?
- 多个组件中共享的问题
- 比如用户的登录状态,昵称,头像,地理位置
- 商品收藏,购物车的物品
- 这些状态信息,可以放在一个对象里面,同意管理,供全局组件使用,重点还是响应式的
# 1.3怎么使用vuex?
使用步骤:
- 安装vuex
npm i vuex - 创建store(仓库)文件夹
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 安装插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
counter:0
},
mutations:{
increment(state){
state.counter++
},
decrement(state){
state.counter--
}
},
actions: {
}
})
// 导出对象
export default store
// 取出store
$store.state.counter
// 修改装状态 .vue中
add() {
this.$store.commit('increment')
}
sub() {
this.$store.commit('decrement')
}
修改状态:
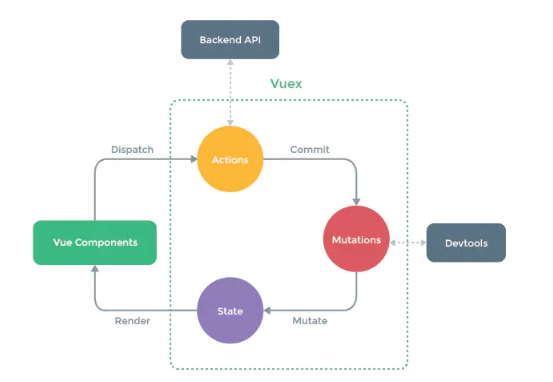
- 正确的做法应该分发一个行为(dispath)到Actions里面
- 然后由Actions提交(commit)到Mutations里面,actions里面可以处理异步操作,Actions连了Backend API
- 再由Mutations改变(mutate)改变state
// 错误用法:
$store.state.counter++
为什么修改过程需要这么复杂呢?
- 通过Devtools可以跟踪状态的修改
- 知道是谁修改了状态,好判断哪里出了BUG
# 1.4vuex的核心概念
vuex中有5个核心概念:State、Getters、Mutation、Actiuon、Module
# 1.4.1 State单一状态树
什么是单一状态树呢?就是单一数据源,只创建一个store便于管理
# 1.4.2 Getters基本使用
Getters类似于vue中computed计算属性,有些时候,我们需要从store中获取一些state变异后的状态,比如取出年龄大于35岁的老程序员
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
programer: [
{name: 'aaa', age: 28},
{name: 'bbb', age: 25},
{name: 'ccc', age: 37},
{name: 'ddd', age: 36},
]
}
})
// 计算属性computed
computed: {
getOldProgramer() {
return this.$store.state.programer.filter(age => age >= 35)
}
}
// getters
getters: {
getOldProgramer() {
return this.$store.state.programer.filter(p => p.age >= 35)
}
}
# 1.4.3Mutation状态更新
官方明确指出,修改状态必须要通过mutations
Mutation主要包括两个部分:
- 字符串的事件类型
- 一个回调函数,该回调函数的第一个参数就是state
例子:
- increment和decrement是事件类型
- 后面的函数是回调函数
mutations:{
increment(state){
state.counter++
},
decrement(state){
state.counter--
}
},
通过mutation更新:
- 需要在.vue中通过commit
- 可以进行传参
// 不传参提交
increment: function() {
this.$store.commit('increment')
}
// 传参提交 .vue
increment: function(count) {
this.$store.commit('increment',count)
}
// store中
increment(state, count) {
state.counter += count
}
mutaions特殊的提交风格:
- 上面的代码就是普通提交风格
- 下面代码是特殊提交风格,通过传入对象形式
mutations: {
increment(state,payload) {
this.$store.commit({
type: 'increment', // 上面早就说过,这是个字符串的事件类型
count: count
})
}
}
# 1.4.4 actions
进行异步操作的话,直接通过mutations修改是可以修改,但是无法跟踪状态,这个时候就需要添加一步操作,actions
actions: {
aUpdateInfo(context) {
// 异步操作
context.commit('updateInfo')
}
}
mutations: {
updateInfo(state) {
state.info.name = 'qmj'
}
}
// .vue中
uodateInfo() {
this.$store.dispath('aUpdateInfo')
}
# 二、Vue-router
# 2.1 跳转页面不刷新
可以用hash进行路由跳转
- 可以用history.pushState({},'',"home"), history.back()
- history.replaceState({},'','home') 这样不可以进行返回
- history.go(-2)可以连续返回两个页面,正数就是前进
- history.forward() 就是前进一个页面 相当于go(1)
# 2.2动态路由
映射表中:
path: '/user/:userId'
.vue中
<router-link :to="'/user/'+userId"></router-link>
data() {
return {
uerId: 'qmj'
}
}
可以通过this.$route.params.id拿到用户id
# 2.3路由懒加载
# 为什么要懒加载?
- 一个项目中页面很多,组件更多
- 打包后都会在一个js文件中,造成这个页面非常大
- 一下子请求全部组件的话消耗性能,出现短暂空白
- 需要加载时菜让他加载,就叫懒加载
# 懒加载做了什么?
- 将路由对应的组件打包成一个个的js代码块
- 在这个路由被访问到时,才会加载对应组件
# 路由懒加载的写法
// 推荐写法,ES6
const Home = () => import('../components/Home.vue)
# 2.4路由的嵌套
# 路由嵌套应用场景
- 在home页面中,希望通过/home/news和/home/message访问一些内容
- 一个路径映射一个组件,访问这两个路径也会分别渲染两个组件
# 嵌套配置方法
配置信息
{
path: '/home',
component: Home,
children: [
{
path: 'news',
component: News
},
{
path: 'message',
component: Message
}
]
}
// 在Home.vue中站位符
<router-view></router-view>
# 2.5路由传参
: : : tip
传递参数主要有两种方式: params 和 query
: : :
# 方式一——params
- 配置路由格式 /user/:id
- 传递方式: 在path后面跟上对应的值
- 传递后形成的路径: /user/123
# 方式二——query
- 配置路由的格式:/user,就是普通配置
- 传递方式: 对象中使用query的key作为传递方式
- 传递后形成的路径:/router?id=123,/router?id=abc
<router-link :to='{path: '/profile', query: {name:'qmj',age:18}}'>档案</router-link>
# 相关应用
// 点击跳转
userClick() {
this.$router.push('/user/'+this.suerId)
}
//
profileCilck() {
this.$router.push({
path: '/profile',
query: {
name:'qmj'
}
})
}
← VUE语法 vueDiff算法学习 →